With the sharp increase in China's power demand, the development potential and market prospects of nuclear power are gradually emerging. The development of nuclear power has become an important measure to accelerate the adjustment of China's energy structure. By 2020, the installed capacity of China's nuclear power will reach 40 million kW, which gives China's machinery. Manufacturing companies have brought historic development opportunities. With the rapid development of nuclear power industry, the requirements for steel for nuclear power are also increasing. Z2CN18-10 is a French austenitic stainless steel of RCC-M220 standard. It has excellent resistance to intergranular corrosion and good mechanical properties and is widely used in nuclear power flanges and pipes. However, the steel is a single-phase austenitic stainless steel, and austenite and a small amount of ferrochrome carbide are always maintained during the forging process, and no phase transformation occurs, and the grain size and mechanical properties cannot be changed by the final heat treatment. The steel is different from ordinary carbon steel in that it has low plasticity and large deformation resistance during forging, which is 1.6 to 2 times that of ordinary carbon steel, has a small forging temperature range, strong crack sensitivity, and is difficult to produce. There are also few applications, and there are few documents available for review, which brings great difficulties to the production of forgings.
Recently, our company received a batch of nuclear power coolant storage box flange, the flange size is 4000mm × 3782mm × 345mm, the material is Z2CN18-10, the chemical composition is shown in Table 1.
1. Early technical preparation
First, determine the reheating temperature of the Z2CN18-10 forging. Since austenitic stainless steel cannot change the grain size and mechanical properties by heat treatment, grain refinement can only be achieved by forging, the heating temperature is too high, and the crystal grains grow sharply, and a suitable heating temperature must be found. To this end, 13 samples were selected and heated in an electric furnace of the laboratory for 1 h, and the grain size was measured after rapid cooling. The 13 samples were respectively heated to 800 ° C, 850 ° C, 900 ° C, 950 ° C, 1000 ° C, 1050 ° C, 1080 ° C, 1100 ° C, 1120 ° C, 1140 ° C, 1160 ° C, 1180 ° C, 1200 ° C. By comparison, it is found that the grain size below 1080 ° C has almost no change, the crystal grains grow rapidly from 1100 to 1160 ° C, and the crystal grains grow sharply above the temperature of 1180 ° C. Through the above test, it can be determined that the temperature of 1050 ° C and below is a suitable temperature for forging and reheating.
Secondly, based on past experience, we know that the as-cast microstructure of steel ingots is inferior to forged microstructures, and it is easy to crack when upsetting, so it is lightly pressed during the first fire forging, breaking the primary and transverse crystal shells and breaking them. Casting the structure to improve hot workability. Now adopt a new process, using a steel plate to roll a steel cylinder to cut the steel ingot, wrap the whole package, and leave a venting hole at the upper and lower ends. This process has two advantages: First, the steel ingot has this protective layer. The furnace flame cannot be sprayed directly onto the forging to prevent over-burning, decarburization and cracking. Second, there is this protective layer. The steel ingot is not in direct contact with the upper and lower anvil of the hydraulic press. The steel ingot does not locally cool, which prolongs the forging time and solves the problem of narrow stainless steel forging interval, thereby reducing the trouble of preheating tooling.
2. Production process
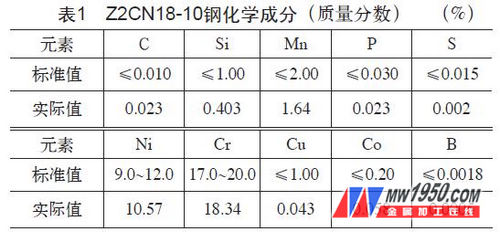
(1) Through the above technical preparation, the process route for formulating the Z2CN18-10 coolant storage tank flange is: heating after electroslag remelting ingot wrapping→40MN hydraulic press forging→water cooling after forging→size inspection→roughing→UT→solid Dissolution treatment → performance test → finishing → ultrasonic inspection → inspection packaging, forging process is shown in Table 2. Forging with a 40MN hydraulic press, the first fire heats the steel ingot to 1250 °C, and the large deformation amount is rough and punched, eliminating the internal defects of the steel ingot, and then heating to 1150 ° C for reaming, and finally heating at 1050 ° C to suppress the grain re Growing up to ensure that the last fire forging ratio is >1.2.
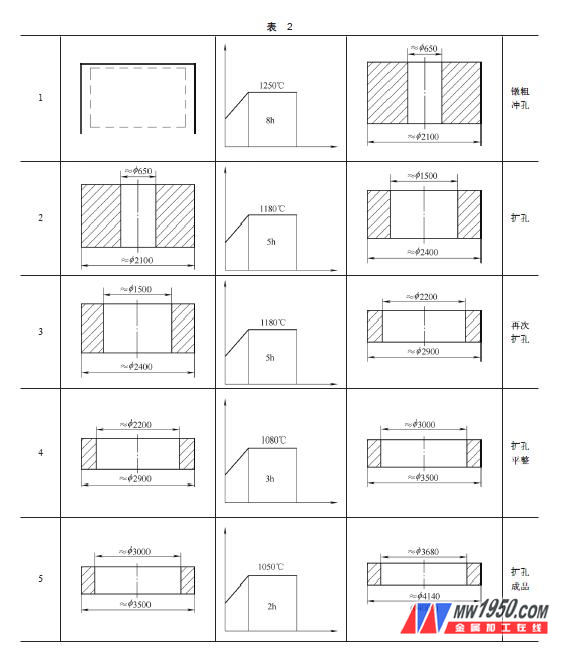
(2) After solution treatment, the solution treatment is carried out to eliminate the carbides generated during the forging process, and the process is as shown in the drawing.
(3) Ultrasonic testing was carried out according to the RCC-MMC2000 standard, and no defects were found in the penetration test according to the RCC-M4000 standard.
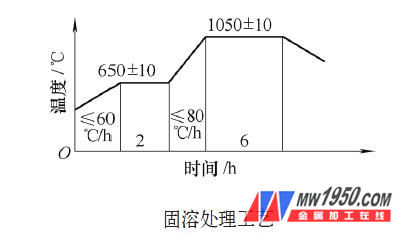
(4) The test results of mechanical properties after solution treatment are shown in Table 3.
3. Conclusion
Through the wrapping treatment of the steel ingot, the heating temperature and the reheating temperature of the furnace are clarified, and a reasonable process route is implemented, so that the indexes of the coolant storage tank flange meet the requirements of the user.
Water Supply Pump Sets,Water Supply Pump,Supply Water Pump,Multistage Pump Set
Shanghai NuoSai Pump Manufacturing Co., Ltd. , https://www.nuosai.net