Phosphating of aluminum and aluminum alloys pre- treatment of aluminum and aluminum alloy parts prior to coating can enhance the bond between the coating and the workpiece. The pretreatment methods are chemical oxidation, anodization, and phosphating. The phosphate treatment of aluminum is similar to the phosphating treatment of steel parts, but an appropriate amount of fluoride should be added to the phosphating solution, and the main component of the obtained film layer is zinc phosphate. However, the phosphate film on the surface of aluminum and aluminum alloys has poor corrosion resistance and cannot be used for protection, but is used for the bottom layer of electrophoretic paint. Aluminum and aluminum alloys are relatively easy to phosphatize, and zinc phosphating and chromate monophosphate can be used together. The two methods differ in solution characteristics and film properties, but the film formation process is very similar.
Phosphating treatment of titanium and titanium alloys Titanium and titanium alloys are light in weight and high in mechanical strength. They are used in industrial, national defense, aerospace and aerospace applications, and are mainly used to manufacture shells and parts for various devices. Titanium and titanium alloys are easily oxidized to form a protective oxide film in a natural state, and the film structure is dense, so the adhesion is poor when the surface is coated with an organic coating. In addition, the natural oxide film on the surface of titanium and titanium alloy is thin, and it is easily damaged during processing and transportation, resulting in more serious corrosion. In order to improve the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of titanium and titanium alloys, conversion coating treatment such as chemical oxidation, anodization, phosphating, etc. may be performed on the surface thereof. Phosphating films of titanium and titanium alloys enhance the bonding between the surface of the workpiece and the coating layer of the organic coating. In addition, the phosphating film on the surface of titanium and titanium alloy has a good lubricating effect, and can be used for stamping and drawing of magnesium alloy workpieces, and achieves good lubrication and wear-resisting effects. After the phosphating treatment, the phosphating layer is sealed, and the phosphatized parts can be immersed in oil or soap liquid for a certain period of time to achieve the purpose of sealing.
Titanium and titanium alloy phosphating solution formulations and process conditions are shown in Table 2-30.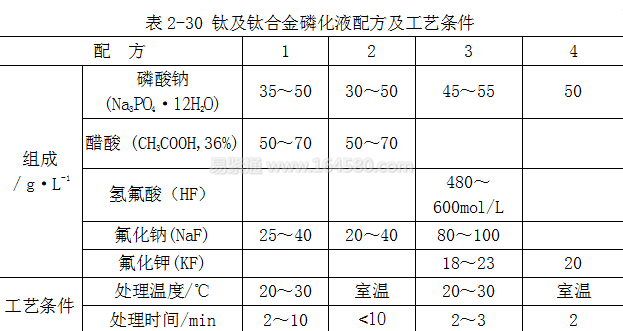
Magnesium alloy phosphating magnesium is relatively active in chemical properties, has poor corrosion resistance to the environment, and is easily oxidized on the surface. It is often incorporated into other metals to form magnesium alloys. The magnesium alloy has a small density, high strength, good mechanical properties, and also has a good shielding effect on electromagnetic waves, which can effectively reduce noise and reduce vibration. At present, magnesium alloys have been widely used in automobile manufacturing, electronic communication, decoration and decoration, household appliances, aviation, aerospace and other fields.
In order to improve the decorative properties of magnesium alloy products and enhance the corrosion resistance of magnesium alloys, it is necessary to finish and coat the surface, such as oxidation, passivation, phosphating, anodizing, etc., to form a conversion film, or to coat organic coating.
In general, the magnesium alloy is treated with chromate, and the obtained oxide film has good corrosion resistance; the phosphating film obtained by phosphating the magnesium alloy with phosphating salt is inferior to the chromate film. It was rarely used in the past. In recent years, with the increasing emphasis on environmental protection, the use of chromate has been limited. Therefore, the use of phosphating to replace chromate oxidation is the key direction for the development of magnesium alloy surface treatment.
A. Magnesium alloy phosphating formula and process conditions The phosphate conversion film on the surface of magnesium alloy includes phosphate/potassium permanganate, zinc phosphate, zinc-calcium phosphate and the like. The formula and process conditions of several magnesium alloy phosphating solutions are shown in Table 2-31.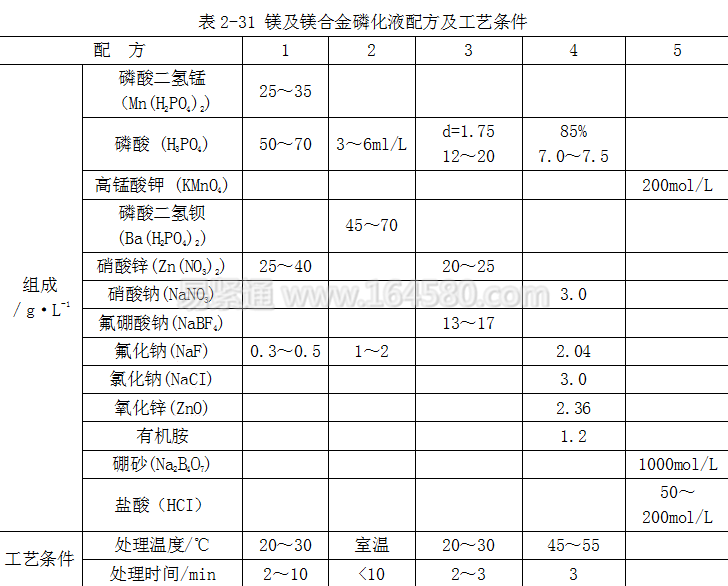
In addition to the treatment of magnesium alloy by chemical phosphating, a better quality phosphating film can be obtained by electrolytic phosphating. The formulation and process conditions of the electrolytic phosphating solution are shown in Table 2-32.
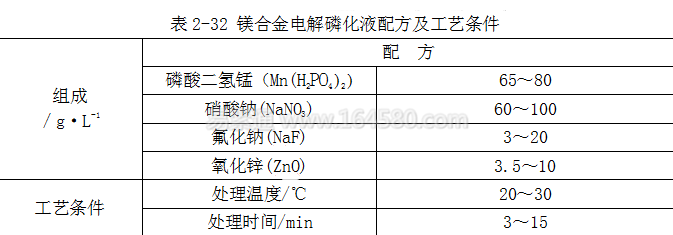
B. Magnesium alloy film properties Magnesium alloys are treated with phosphate conversion or phosphate/permanganate conversion. The biggest disadvantage is that the solution is consumed quickly. It is necessary to constantly adjust the concentration and acidity of the phosphating solution, so high manganese The application of the acid salt/phosphoric acid system is greatly limited.
Depending on the composition of the phosphate, when magnesium and magnesium alloys are phosphated, two different types of layers are formed on the surface. When the alkali metal salt or ammonium salt of phosphoric acid is used as the treatment liquid, the phosphate obtained on the surface of the workpiece is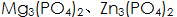 Or an oxide film, that is, a phosphating conversion film. The phosphating solution contains free phosphoric acid and dihydrogen phosphate (such as
Or an oxide film, that is, a phosphating conversion film. The phosphating solution contains free phosphoric acid and dihydrogen phosphate (such as 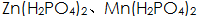 When the accelerator is used, the surface energy can be obtained from a divalent metal ion, a hydrogen salt or an orthophosphate.
When the accelerator is used, the surface energy can be obtained from a divalent metal ion, a hydrogen salt or an orthophosphate. 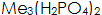 The film composed is called a phosphating pseudo conversion film.
The film composed is called a phosphating pseudo conversion film.
Led street light,outdoor street lamp,all in one street light
Shenzhen You&My Electronic Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.nbyoumysolarlight.com