Abstract: Acidifiers are extremely common feed additives in the feed industry, especially in young animal diets for anti-diarrhea and health promotion. However, in the actual use process, due to the composition of the acidifier product, the amount of additives, animal species, physiological stage, feeding conditions and formulation composition, the effect of the acidifying agent is quite different. In this paper, the physiological functions of the acidifying agent, the mode of action and the factors affecting its effect are reviewed.
Key words: acidifier; physiological function; effect factors;
In modern pig production, in order to improve the performance of sows, most of them are weaned in the early 3-5 weeks, but the digestive system and immune organs of early weaned pigs are not well developed. The gastric acid secretion of piglets can not reach the level of adult pigs for a long time before weaning. After weaning, the lactic acid bacteria in the stomach of piglets can no longer use the lactose in the milk to produce lactic acid, which further reduces the acidity level in the stomach. The direct consequence is that the pepsin activity is greatly increased. Reduce, so that feed nutrients, especially protein digestion and malabsorption, cause feed waste, nutritional diarrhea. It provides a suitable breeding environment for various harmful bacteria in the intestines, and the undigested protein feed also provides a large amount of nutrients to various bacteria when passing through the intestines, causing the pathogens to multiply and explode bacterial diseases. The fundamental measure to solve the above problems is to add an appropriate amount of acidifier to the piglet diet to make up for the physiological acid deficiency of the piglets.
First, the main physiological functions of acidifiers
According to the results of the current research, the main physiological functions of the acidifier mainly include three aspects: adjusting the pH value in the stomach, ensuring that the digestive enzyme exerts its enzyme activity under normal pH environment and inhibits the proliferation of harmful microorganisms in the digestive tract, optimizing the intestinal microflora. Structure to reduce pathogen infection. After the organic acid is absorbed into the body, it also provides a considerable part of the energy to the body, which affects the metabolism of the body.
1. The proper pH in the stomach of an animal is very important for maintaining the activity of digestive enzymes. Adult pigs generally ensure a normal acidic environment in the stomach, while piglets have immature digestive system development due to their unique physiological defects, and gastric acid secretion is seriously insufficient, resulting in a pH in the stomach that is much higher than the pH at which pepsin is active. The suitable pH value of pepsin is 2.0 to 3.5, and when it is more than 3.6, the activity is remarkably lowered; when it is more than 6, it is inactivated. Weaned piglets have a pH greater than 4.2. Therefore, the protease activity in the stomach of piglets cannot be fully exerted, and the digestibility of protein feed is reduced, which may cause a series of digestive diseases such as diarrhea in piglets. In addition, the pH value of the commonly used piglets in China is 5.8-6.5. Therefore, the diet will also contain limited gastric acid secreted by piglets, which will aggravate the digestive diseases caused by insufficient stomach acid. Studies have shown that the addition of acidifiers to the diet can effectively reduce the pH of the diet itself and thus reduce the pH of the digestive tract of piglets. However, some scholars have shown that the pH value of the diet after adding acidifier can be reduced from 5.95 to 4.71 (P<0.01). However, the addition of acidifier in the feed did not significantly reduce the pH of the stomach (P>0.05). The acidified diet treated the pH of the stomach was 3.66, while the pH of the unacidified diet was 3.73. . Rothd (1992) found that: the intestinal pH of pigs fed an acidified diet was generally higher than that of the control group; however, the results of the Risley study showed that the intestinal pH of pigs fed acidified diets was lower than that of the control group, while Eidelsburger believed Both high and low results will appear and are inconsistent. Therefore, the acidifier can only reduce the acidity of the feed to a certain extent, and make up for the deficiency of gastric acid secretion. However, the relationship between the type and level of acidifier added to the diet and the amount of gastric acid secretion in the animal is unclear.
At present, the amount of acidifier added to the diet has not been standardized, and there is no basis for addition. The use is relatively blind. According to the research, it is determined that the addition amount of acidifier can determine the addition amount of acidifier required to maintain the acidity of digestive tract based on the acidity of the diet, and it is considered that the digestive physiology of piglets when the acidity is 20mmol/100g. Most suitable, can significantly increase pepsin activity. Acidity is too low (less than 100mmol / 100g) will cause acidosis. When the acidity of the diet is reduced to about 20mmol/100g diet, the addition amount of the pure organic acid complex acidifier is mostly 1% to 3%, and the acidifier of the inorganic acid and the organic acid is more acidic. The amount is mostly 0.1% to 1%. Therefore, in practical applications, the optimal addition amount of the acidifier should be determined according to the type of acidifier and the acidity of the basal diet.
2. Adding an acidifying agent to the diet helps the animal's digestive tract micro-ecological balance. The addition of an acidifying agent to the diet can lower the intestinal pH. The suitable pH value for the growth of concentrated pathogenic bacteria is neutral alkaline, while the beneficial bacteria such as lactobacilli are suitable for acidic environment reproduction. At the same time, lactic acid, which is a metabolite of beneficial bacteria such as lactic acid bacteria, also has an inhibitory effect on Escherichia coli. Therefore, the acidifier helps the intestinal microflora structure to optimize the reduction of pathogenic bacteria infection, is beneficial to the establishment of intestinal micro-ecological flora balance, and cultivates a healthy intestinal tract for animals. One of the modes of action of organic acid antibacterials is to reduce the pH of the digestive tract by ionizing hydrogen ions, thereby destroying the suitable living environment of harmful bacteria. Another way is to rely on the undissociated organic acid molecules penetrating the cell wall of the Gram-negative bacteria into the cells, and then these organic acid molecules dissociate the mutual hydrogen ions and acid ions in a relatively alkaline environment in the bacteria, Hydrogen ions reduce the pH inside the cells, and in order to restore the balance of their own pH, the cells release protons, which will digest their own energy and cause a lot of energy loss. In addition, acid ion accumulation will directly interfere with and block the synthesis of DNA in the nucleus. This dual mechanism of organic acids effectively inhibits the growth of bacteria. VFA serves as an important indicator of growth in microbial activity. Some studies have reported the effect of acidifiers on VFA levels in the gut. Gabert et al. (1995) did not detect significant changes in VFA content in the intestine after adding 1% formic acid to piglet diets. The addition of 1.5% fumaric acid or citric acid to the diet of weaned piglets did not significantly affect VFA content in the gastrointestinal tracts (Risley et al., 1992). Although the effect was not significant, the succinic acid content in the stomach of weaned piglets fed fumaric acid increased, indicating that microbial activity was altered. Blank et al. (2001) found that the addition of fumaric acid to the diet of weaned piglets reduced the content of lactic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, ammonia and spermidine in the ileal chyme, and this effect was related to fumaric acid. The level of addition is related. This effect disappears when the acidity of the diet increases. As can be seen from the above studies, the influence of acidifiers on microorganisms and their fermentation products in the intestines is controversial. Metzler and Mosenthin (2007) reviewed a large number of studies and pointed out that organic acids can improve the performance of weaned and fattening pigs and reduce the risk of disease, but the research on its mechanism of action is still ongoing, and there are still many problems. Not stated.
3. After the organic acid is absorbed into the body, it also provides a considerable part of the energy for the body. The organic acid is absorbed by the intestinal epithelial cells in a passive diffusion manner. Short chain organic acid molecules produce ATP through the citric acid cycle. For example, 1 mole of fumaric acid can produce 18 moles of ATP. The energy content per mole of fumaric acid is 1340 kJ, so about 74.4 kJ of energy is required for each mole of ATP produced, which is similar to the energy consumed by ATP production from grapes. Thus, in terms of energy efficiency, fumaric acid and glucose may be equivalent, as is citric acid. When acetic acid and propionic acid produce equal amounts of ATP, they need to consume 18% and 15% more energy, respectively (Kirchgessner and Roth, 1988). In view of the fact that the ATP produced by the organic acid during the metabolic process is completely usable, the energy contribution of the organic acid should be considered when the amount of organic acid added to the diet is large. For example, propionic acid has an energy content six times that of wheat (Diebold and Eidelsburger, 2006).
Second, the factors affecting the effect of acidifiers
1, adding types and doses
Different acidifiers have different effects on physical and chemical properties and biological properties. For example, fumaric acid has strong inactivation activity against Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Escherichia coli, and has no inhibitory effect on lactic acid bacteria; formic acid, Salmonella propionate, fungus, fusiform Bacillus, Bacillus and Gram-positive bacteria have strong inhibitory effects; sorbic acid can effectively inhibit the growth of yeast and mold, but it is beneficial to the growth of beneficial microorganisms. It is recognized that there are mainly citric acid, fumaric acid and calcium formate. From the perspective of increasing daily gain and feed efficiency, citric acid > fumaric acid > calcium formate. Most of the single propionic acid, butyric acid, malic acid, hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid proved to be ineffective or even negative. It is generally believed that an appropriate amount of acidifier will have a significant growth-promoting result. The addition amount is insufficient to achieve the desired effect, such as the pH cannot be lowered to an appropriate level to more fully increase the activity of the digestive enzyme. Excessive addition will affect palatability and destroy the acid-base balance, which will lead to serum alkali storage in piglets, increased HCO3-concentration, and increased pH of stomach and small intestine contents. To some extent, it causes metabolic acidosis.
2, the composition of the diet is different
Diet is the main exogenous factor affecting the acidity of digestive tract in piglets. The acidity of the diet is an important factor, and the acidity of the diet of piglets is closely related to the selection of raw materials and the determination of nutrient levels. The acidity of different feed ingredients is different, among which the mineral materials have the highest acidity, the animal raw materials are the second, and the vegetable feed ingredients have lower acidity. The addition of fumaric acid to low buffer diets increased the digestibility of ileum CP, GE and major amino acids. Dietary protein levels are also an important factor affecting the effectiveness of acidifiers. It is reported that 2% of fumarate is added to the two diets with crude protein levels of 16% and 20%. The average daily gain of the 16% protein group is 281 g, and the feed efficiency is 0.49, while the latter are 329g and 0.62, respectively. At the same time, different protein sources in the diet require different acidity conditions in the gastrointestinal tract to achieve optimal digestion. For example, milk products require a pH of 4.0, soy meal and fish meal require a pH of 2.5, and the protein is the stomach. A strong inhibitor of pH change, excess protein reduces the effectiveness of the acidifier.
3, the impact of the use phase
The effect of adding acid preparations on piglets is mainly in the early stage of weaning. Two weeks after weaning is better than the next two weeks, the effect is less obvious (Eckel, 1997). This is because the piglets in the early weaning period have a certain ability to secrete hydrochloric acid, but the secretion is insufficient. After the piglets are fed, the pH of the stomach will rise to more than 5, resulting in indigestion and diarrhea in the piglets. Gromevell (1985) found a linear correlation between stomach acid production and body weight from birth to 5-6 weeks of age. The effective time is generally between pre-weaning and 25-30 kg body weight.
4, the impact of the breeding environment
The sanitary conditions, stocking density, temperature and humidity, light and various stress factors of the pens also affect the use of organic acid preparations. The poorer the feeding conditions, the better the use of organic acid preparations.
Third, the application prospects of acidifiers
The addition of an acidulant to the feed has been considered to be beneficial to the growth of pigs. Previous studies have confirmed that acidifiers can improve pig performance and health, and the latest research data also validates this effect. Acidifiers have been recognized as one of the most effective ways to replace antibiotics for growth promotion on pig feed. Therefore, there are currently a large number of acidifier products to improve the performance and health of pigs. Acidifier products commonly found on the market include a variety of active ingredients and forms. Most of the products are complex acids, including combinations of various organic acids or combinations of organic and inorganic acids. Monoacid products are also available on the market. Fumaric acid, lactic acid, citric acid and phosphoric acid are the most common components in acidifier products. At present, in order to solve the effect that the acidifying agent can finally reach the function of the hindgut, a coating type acidifying agent appears on the market, which not only reduces the use amount of the acid preparation, reduces the cost, but also uses the effect better than the adsorption type product, and can also reduce the effect thereof. Corrosion of feed processing machinery. However, there are few reports on the application of such acidifiers, and the use effect needs further evaluation.
At present, the research on acidifiers at home and abroad mainly focuses on the determination of acid binding ability of feed and the effect of acid strength on young production performance, but lacks the quantitative relationship between feed acid binding ability and composition ratio. Therefore, it is difficult to determine the level of addition of the acidifying agent when the acid binding capacity of the feed reaches an optimum level. Acidifiers have good advantages in improving feed utilization, reducing disease occurrence, pollution-free, and no residue. They have become a competitive alternative to non-pharmaceutical additives to replace or partially replace antibiotics as growth promoters. The EU is currently looking forward to replacing it with antibiotics soon. It is believed that with the further deepening and wider application of relevant acid preparation research, it will certainly bring us greater economic and social benefits.
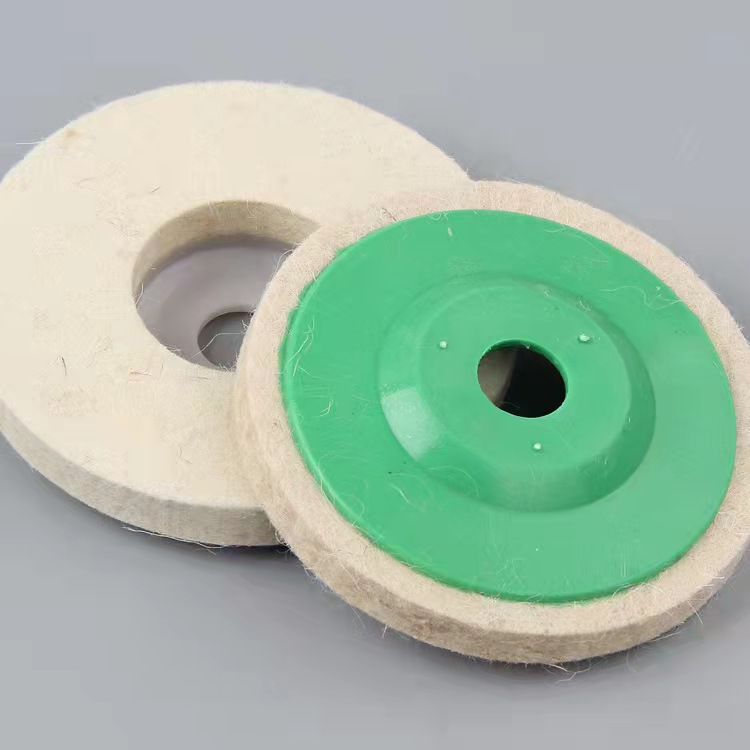
Wool Felt Wheels
The stone/ceramic grinding wheel is made of non woven cloth and high pressure binders with high quality. The polymer fiber material is refined by precision equipment. The material has an open mesh structure, flexible and durable, and the sand grain is beautiful and even.The grinding blade is even, sharp and durable, stable quality, long service life, high working efficiency, environmental protection, non-toxic and non-fading, it is the international advanced stone grinding material.The grinding wheel is generally installed in mould head of special automatic machine, widely used in the stone/ceramic/tile processing and production industry, can be used for a variety of material surface treatment, such as a variety of ceramic, tile and artificial stone etc, to achieve a very high degreed of finish. it`s as a support material for waxing when polishing.
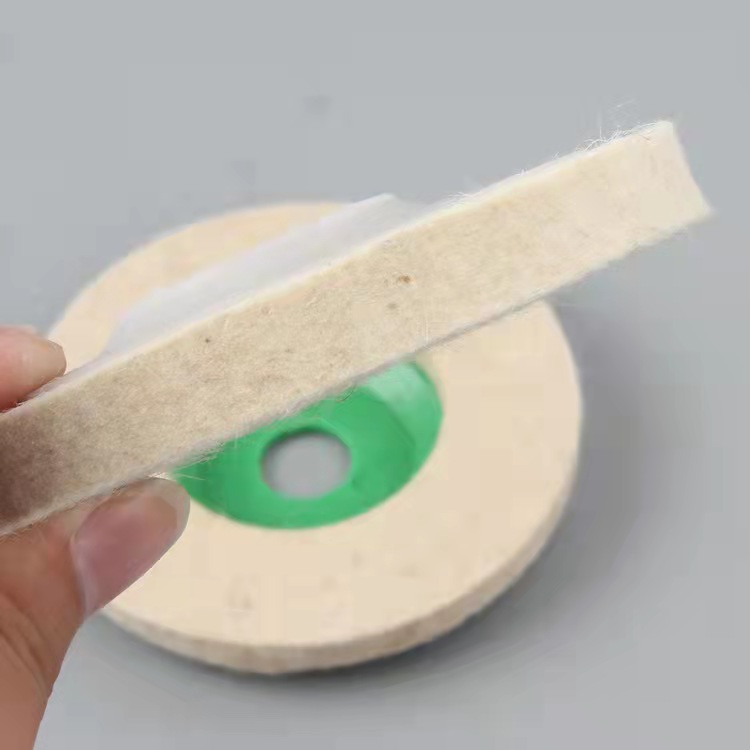

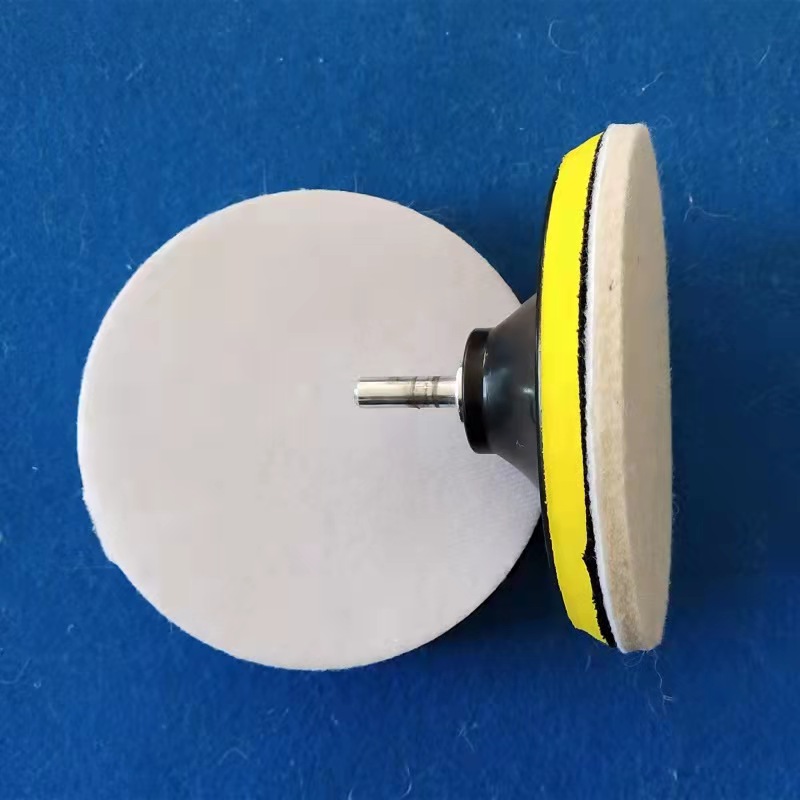
Our Wool Polishing Pads made of 100% premium pure wool with designed reasonable make buffing and waxing more easily. Our Wool Polishing Pads made of 100% premium pure wool with designed reasonable make buffing and waxing more easily. Wool felt wheel made from high quality wool felt material, it's perfect for fine finish polishing on stainless steel, glass, ceramic, metal, marble etc.... we have a wide range of all kinds of wool felt wheel with different shapes, sizes and designs for different applications.
We distributes and wholesales various brands of Bonded Abrasives , Abrasive Sanding Disc, Cutting Wheels , Flap Wheels , Flap Disc Backing Pad, Flap Disc Adhesive, and Surface Conditioning Product etc, and enjoy a high position among consumers.
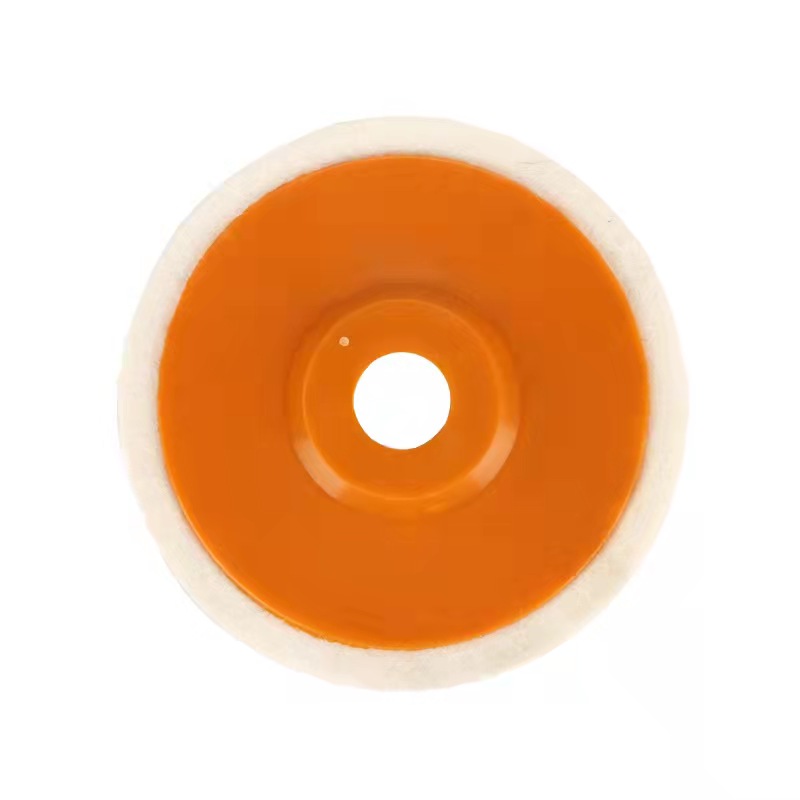
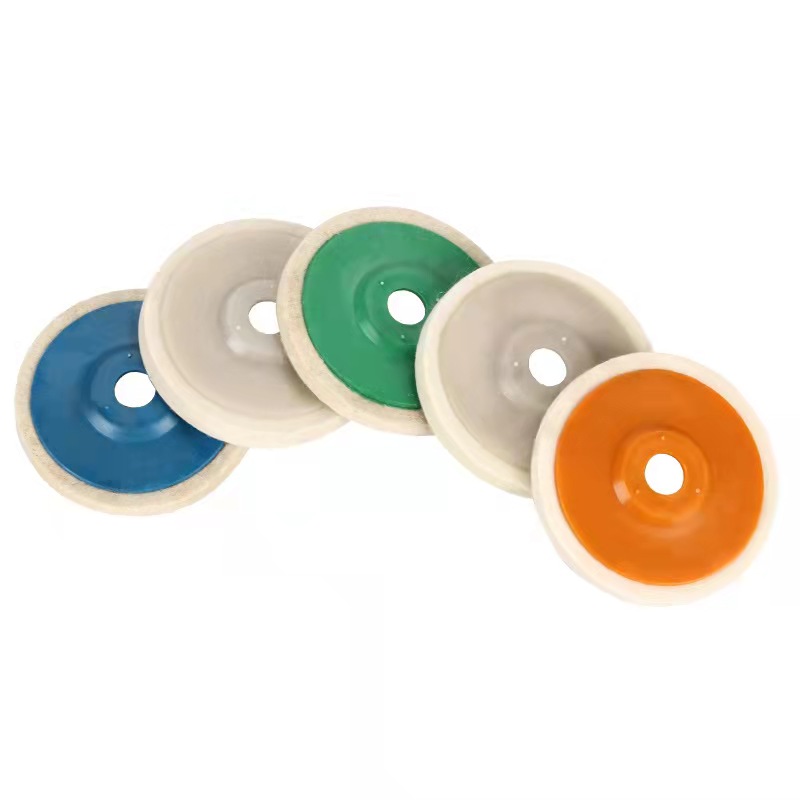




Wool Felt Wheels,Wool Polishing Wheel,Wool Felt Polishing Wheel,Wool Felt Disc Polishing Wheel
Zhengzhou Jiading Abrasive Manufacturing Co.,Ltd , https://www.jiadingabrasive.com