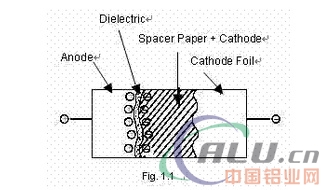
[China Aluminum Network] The following figure shows the basic structure of an aluminum electrolytic capacitor, which consists of an anode, an aluminum layer composed of aluminum oxide attached to an insulating medium, a cathode aluminum layer of a receiving electrode, and a real electrolyte. Constituted cathode. The electrolyte impregnates the paper between the two aluminum layers.
Why can't electrolytic capacitors withstand reverse voltage
The aluminum oxide layer is electroplated on the aluminum layer and is very thin with respect to the voltage applied to it, and is easily broken down, resulting in capacitor failure.
The aluminum oxide layer can withstand positive DC voltage, and if it is subject to reverse DC voltage, it can easily fail within seconds. This phenomenon is called 'Valve Effect'. This is the reason why aluminum electrolytic capacitors have polarity. If both electrodes of an electrolytic capacitor have an oxide layer, a nonpolar capacitor is formed.
Many articles have reported the mechanism of the threshold phenomenon of the reverse voltage of the aluminum electrolytic capacitor, called the hydrogen ion theory. When the electrolytic capacitor is subjected to reverse DC voltage, the cathode of the electrolyte is subject to forward voltage and the oxide layer is subject to negative voltage. The hydrogen ions collected in the oxide layer will pass through the medium to the boundary between the medium and the metal layer and be converted into hydrogen gas. The expansion force of hydrogen causes the oxide layer to fall off. Therefore, the current flows through the electrolyte directly after the breakdown of the electrolyte and the capacitor fails. The DC voltage is very small. Under the effect of a 1~2V reverse DC voltage, the aluminum electrolytic capacitor will fail immediately due to the hydrogen ion effect in a few seconds. On the contrary, when the electrolytic capacitor is subjected to a forward voltage, negative ions concentrate between the oxide layers because the diameter of the negative ions is so large that they cannot break through the oxide layer, so they can withstand higher voltages.
Glossary:
1. Anode: An anode aluminum layer, the positive electrode of an electrolytic capacitor. 2. Cathode: The electrolyte layer.
Dielectricdi: An aluminum oxide layer attached to the surface of the aluminum layer.
4. CathodeFoil: It connects the electrolyte and the outer layer. This layer does not need to be oxidized in the production, but in practice, because the aluminum is easily oxidized during the etching process, it forms a naturally oxidized oxidation. Layer, this oxide layer can withstand 1 ~ 2v voltage.
5. Insulation paper (spacer paper): Separation of the cathode and the anode so that they do not short-circuit directly and adsorb a certain amount of electrolyte.
What happens when there is a reverse polarity capacitor?
If the capacity of the capacitor is small, the withstand voltage is high, and the operating voltage is low, the reverse connection will not show up. If the capacity is slightly larger (above 100 UF), the withstand voltage is close to the operating voltage, and the capacitor will not be worse than 10 minutes. The form of expression is: bulging, blowing, then exploding.
The reverse polarity of a polar capacitor will explode. Does it mean that it cannot be directly connected to an AC power supply?
Can not be connected to the AC power supply, because this polar capacitor design is used on the DC power supply for filtering purposes, I also asked this kind of question, thought for a long time, has been asking, "Capacitor is not isolated, How can a polar capacitor not be used in an AC power supply?" Because this polar capacitor has special substances inside it, this material cannot withstand back pressure. If it passes to the AC, it will reverse breakdown or explosion.
There is a polarity capacitor can not be reversed. Why does it allow negative half cycle through?
The AC signal can be treated as a short circuit under certain conditions. How to solve the negative half cycle of the AC signal? Do you want to pull up to DC?
The AC signal must be carried on DC current. It is to be pulled up to DC!
When there is a polar capacitor, the positive electrode potential must be higher than the negative electrode. Otherwise, the capacitor leaks - if the circuit is unable to work, the capacitor will explode.
Why does the polar capacitor short circuit?
The internal structure of the polar capacitor is divided into a positive electrode, a dielectric layer, and a negative electrode. The dielectric layer has a unidirectional conductive property. Of course, the product dielectric layer will not be insulated after the reversal, and the capacitor will naturally short-circuit.
Why does the resistivity decrease when the positive and negative electrodes of the electrolytic capacitor are reversed?
When it comes to the principle of electrolytic capacitors: when connected positive capacitor will form a very thin oxide film (alumina) as a dielectric; reverse when the metal aluminum sheet (capacitor positive) is connected to the negative electrode, will electrolysis out H2 An oxide film is formed, and the other electrode does not form an oxide film that can be used as a dielectric because of different materials.
The aluminum electrolytic capacitor consists of anodized aluminum foil that has been etched and forms an oxide film, and an etched cathode aluminum foil.
After the electrolyte paper is wound around, it is impregnated with the working electrolyte and then sealed in an aluminum shell. Due to the polarity of the electrolytic capacitor, it is necessary to pay attention to the correct connection between the positive and negative electrodes when using it. Otherwise, not only the capacitor will not function, but also the leakage current will be large. Within a short time, the capacitor will generate heat, destroy the oxide film, and then damage.
Electrolytic capacitor is a type of capacitor. The medium is coated with electrolyte and has polarity. It can't be connected incorrectly. The electric capacity consists of two metal poles with an insulating material (medium) sandwiched between them. Electrolytic capacitor features: The capacitance per unit volume is very large, tens to hundreds of times larger than other types of capacitors. Electrolytic capacitor features two: rated capacity can be very large, can easily do tens of thousands of μf or even a few f (but not with double layer capacitance ratio). Electrolytic capacitor features three: The price is overwhelmingly superior to other types, because the constituent materials of electrolytic capacitors are common industrial materials, such as aluminum and so on. The equipment for manufacturing electrolytic capacitors is also an ordinary industrial equipment, which can be produced on a large scale and the cost is relatively low. Electrolytic capacitors are usually made of metal foil (aluminum/niobium) as the positive electrode, and the insulating oxide layer (aluminum oxide/niobium pentaoxide) of the metal foil is used as the dielectric. The electrolytic capacitor is divided into aluminum electrolytic capacitors and tantalum electrolytic capacitors by its positive electrode. Capacitors. The negative electrode of an aluminum electrolytic capacitor is composed of a thin paper/film or electrolyte polymer impregnated with an electrolyte solution (liquid electrolyte); manganese dioxide is generally used as a negative electrode of a tantalum electrolytic capacitor. Because the electrolyte is used as a negative electrode (note the difference with the dielectric), the electrolytic capacitor is named. A polar electrolytic capacitor usually functions as a power supply filter, decoupling, signal coupling, time constant setting, and DC blocking in a power supply circuit or an intermediate frequency circuit or a low frequency circuit. Generally can not be used for AC power circuit, when used as a filter capacitor in the DC power circuit, the anode (positive) should be connected to the positive terminal of the power supply voltage, and the cathode (negative) should be connected to the negative terminal of the power supply voltage. , otherwise it will damage the capacitor.
Non-polar electrolytic capacitors are commonly used in speaker divider circuits, TV S correction circuits, and start-up circuits for single-phase motors. Electrolytic capacitors are widely used in home appliances and various electronic products, and have a large capacity range, generally 1 to 1000 μF, and a rated operating voltage range of 6.3 to 450V. The disadvantages are that the dielectric loss and capacity error are relatively large (the larger allowable deviation is +100% and -20%), and the high temperature resistance is poor, and the storage time is long and it is easy to fail.
There is a difference in performance and principle structure between polar capacitors and nonpolar capacitors.
A polar capacitor refers to a capacitor such as an electrolytic capacitor, which is formed by forming two electrodes from an aluminum foil of an anode and an electrolyte of a cathode, respectively, and a layer of an aluminum oxide film produced on the anode aluminum foil as a dielectric capacitor. The structure is made to have polarity. When the capacitor is connected, the aluminum oxide film will remain stable due to the electrochemical reaction. When the connection is reversed, the aluminum oxide layer will become thinner, and the capacitor will be easily broken down. Therefore, the electrolytic capacitor is The circuit must pay attention to the polarity. Ordinary capacitor is non-polarity, you can also connect two electrolytic capacitors anode or cathode in series to form a non-polar electrolytic capacitor.
1, in principle, the same. (1) Both charge and discharge are stored; (2) The voltage on the plate (here, the electromotive force of charge accumulation is called the voltage) cannot be mutated. (3) The difference lies in the difference in the medium, the performance, the capacity, and the structure that lead to different usage environments and uses. On the other hand, according to the needs of production practice, people have experimented with the manufacture of capacitors with various functions to meet the normal operation of various electrical appliances and the operation of new equipment. With the development of science and technology and the discovery of new materials, better and more diverse capacitors will continue to emerge. 2, different media. What is the medium? To put it bluntly, it is the material between the two plates of the capacitor. Most of the polar capacitors use electrolytes as the dielectric material, and usually have the same capacitance as the polar capacitor. In addition, different electrolyte materials and processes produce polar capacitors with the same volume capacity. There is also a close relationship between pressure resistance and the use of dielectric materials. Non-polar capacitor dielectric materials are also many, mostly metal oxide film, polyester and so on. Due to the reversible or irreversible properties of the medium, the use environment of polar and non-polarized capacitors is determined.
3, different performance. Performance is the requirement for use, and greater demand is the requirement for use. If the power section of the TV is filtered with a metal oxide film capacitor, the capacitance and withstand voltage of the filter are required. I am afraid the chassis can only install a power supply. Therefore, only polar capacitors can be used as filters, and polar capacitors are irreversible. That is, the positive electrode must be connected to the high potential terminal, and the negative electrode must be connected to the low potential terminal. General electrolytic capacitor above 1 microfarad, do coupling, decoupling, power supply filtering and so on. Non-polarity capacitors are mostly below 1 microfarad and participate in resonance, coupling, frequency selection, current limiting, and so on. Of course, there are also large-capacity and high-voltage proofing devices, which are mostly used for reactive power compensation, motor phase-shifting, and variable-frequency power supply shifting. There are many types of non-polarity capacitors, which are not repeated one by one.
4, different capacity. It has already been said that the same volume of capacitor media varies in capacity and is not repeated one by one. 5, different structure. In principle, regardless of the discharge of the tip, what shape of the capacitor is required to use the environment can be. The commonly used electrolytic capacitors (with polar capacitors) are round and rarely used. Non-polarity capacitor shapes vary. Like tube shape, deformed rectangle, piece shape, square shape, round shape, combination square shape and round shape, etc., see where it is used. Of course, there are intangible ones. Here, invisible refers to the distributed capacitance. For distributed capacitors in high-frequency and intermediate-frequency devices must not be ignored.
Functionally the same. The main difference is that in terms of capacity, due to the influence of the material structure, the capacity of non-polar capacitors is generally relatively small, generally below 10uF, and the capacity of polar capacitors is generally larger. For example, when performing power supply filtering, you have to use large-capacity polar capacitors.
A basic principle of circuit design is to require the designer to fully understand and master the components in reality. The components used are standard parts and common parts. It is better to have a more common model on the market (the more common the components are, The easier it is to purchase, the greater the supplier's output and the lower the purchase cost. For the components used in the drawings, if only the custom-made materials are available, the cost is certainly not low. If you can not get customized, then this design is equivalent to waste paper.
PS: What you are talking about is the power decoupling capacitor. The large capacitor is suitable for filtering out low-frequency signals, and the small capacitor filters out high-frequency signals (for the principle, see the circuit basis, and the relationship between capacitive reactance and frequency).
However, decoupling is only a function of the capacitor. Capacitors have other functions. Different types of capacitors have different usage characteristics. The capacitor on the schematic is just a symbol, and the techniques behind it are many. This aspect has a lot to do with experience. It cannot be accelerated and can only be accumulated through practice.
In pure AC circuits, only nonpolar capacitors can be used.
In the DC voltage superimposed AC signal circuit, and can guarantee that the superimposed lower voltage does not become negative, you can use a polar capacitor.
In the case of the same capacity, the volume and cost of a polar capacitor are much smaller than those of a non-polarity capacitor. Therefore, if a large capacitance is required, the volume of the capacitor is a big contradiction. The nonpolar capacitor can be used. On occasions, they are naturally replaced with polar capacitors. This not only solves the volume problem, but also has a much lower cost.
Large capacitors can filter out AC signals at lower frequencies. Small capacitors can only filter out signals at higher frequencies. How large a capacitor is needed depends on the frequency of the signal to be filtered and the decibel to be filtered.
In general, the presence of an electric field between two conductors creates a capacitance between the two conductors, and how large the capacity of this capacitor is, and the frequency of the electric field, distance, dielectric and power supply between the two conductors. related. In electronic circuits, if the voltage and frequency, the capacity of the capacitor, the "quality factor" of the capacitor, and the mounting conditions have been set, the choice of capacitor will be the decisive factor.
Capacitors are mainly used in electronic circuits; signal coupling, differential voltage characteristics in RC circuits such as integral, tank circuit in the oscillator circuit, bypass, and power supply filtering.
The type of capacitor is divided according to the dielectric inside the capacitor, there is;
1. Air capacitors; Capacitors using air as dielectric, such as; Variable capacitors for "tuning" in radios
2. Paper capacitors; use a special capacitor paper as a dielectric capacitor. 3. Electrolytic capacitors; capacitors using electrolytes as dielectrics. 4. Mica capacitors; Capacitors using natural mica as the dielectric. 5. Ceramic capacitors; single-layer ceramic materials used as dielectric capacitors.
6. monolithic capacitors; also used ceramic materials as a dielectric capacitor, in order to solve the shortcomings of single-layer ceramic capacitor capacity is small, the actual is a capacitor with a plurality of ceramic capacitors in series; 7. polyester capacitor; nylon material used for Dielectric capacitors.
8. A tantalum capacitor; it is made of metal niobium [nÃ] as a positive electrode, diluted with sulfuric acid, etc. as a negative electrode, and a capacitor made of an oxide film formed on the surface of tantalum is used as a dielectric.
9. A tantalum capacitor; a capacitor made of a tantalum metal (Ta) as the anode material. 10. Wound capacitors; is a kind of capacitor that uses metal wires around the dielectric as electrodes, which can be used to adjust the size of the electrode to change the size of the capacitor by changing the number of turns of the wire.
11. Oil-impregnated paper capacitors; Capacitors made of neutral dielectric oil for use in electric power systems. ......
The capacitor is divided into three types: fixed capacitor, variable capacitor and adjustable capacitor.
Most of them are made of fixed capacity.
Variable capacitance; Capacitors that can be freely adjusted within a certain range of capacity, such as those that can be manually tuned in the radio
Adjustable capacitance (also called semi-variable capacitance); Capacitors that can be adjusted within a certain range, such as ceramic dielectric capacitors and wire-wound capacitors.
It cannot be said that “capacity with large capacitance has polarityâ€. This is wrong. For example, capacitors used in the power system for phase angle adjustment and for arc extinguishing in the start-up network are sometimes very large in capacity. , but regardless of polarity.
Are non-polar capacitors the same as non-polar electrolytic capacitors? Not the same thing.
The vast majority of types of capacitors are non-polar, except that electrolytic capacitors have polarity. Among electrolytic capacitors, there are special non-polar electrolytic capacitors. Compared with ordinary capacitors, electrolytic capacitors have a large capacity, low cost, and small size that other capacitors can not match, but electrolytic capacitors are generally polar, and work reliability, pressure resistance, temperature resistance, dielectric loss and other indicators are not as good as Other capacitors. The so-called non-polarity electrolytic capacitors actually pack two identical electrolytic capacitors back to back. This type of capacitor has large losses, low reliability, and low withstand voltage, and can only be used in a few occasions where demand is not high.
Circular emergency ceiling light is according to the type can be divided into maintenance or non-maintenance . It is made of solid polycarbonate material , with protection rating of IP65 , suitable for indoor and outdoor use . It comes with a premium rechargeable lithium-ion battery with automatic monthly and annual detection .

Emergency Light Ceiling,Industrial Emergency Light,Led Emergency Ceiling Lights,Ceiling Mounted Emergency Lights
Jiangmen City Pengjiang District Qihui Lighting Electrical Appliances Co., Ltd , https://www.qihuilights.com